Answer:
c. $865.31
Step-by-step explanation:
Data:
Project S
Initial Outlay = $15,000
Y1 CF = $7,000
Y2 CF = $12,000
Project L
Initial Outlay = $15,000
Y1 to Y4 CF = $5,200
To solve for Project S
In ordered to compare project S with project Project L, we shall prolong it to four years.
cashflow stream will be as follows:
Y0=-$15,000 Y1=$7,000 Y2=-$3,000($12,000 CF - $15,000 outlay for prolonging the project second time) Y3=$7,000 Y4=$12,000
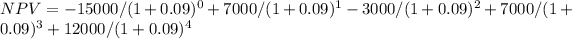
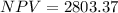
Following is the formula for Equivalent annual annuity
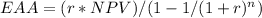
EAA = Equivalent annual equity
NPV = Net present value
r = Interest rate
n = Number of periods
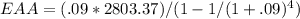
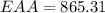
To solve For Project L
In order to calculate present value of the annuity, following formula will be used:
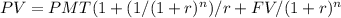
NPV = Initial outflow - Present Value
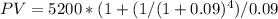
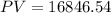
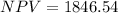
Using the above formula we can calculate EAA:
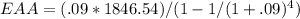
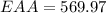
The most profitable EAA is of project S
*all figures are rounded off to two decimal points*