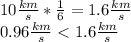Answer:
The water molecule cannot escape, since the average velocity of the water molecules is less than one sixth of the escape velocity of venus.
Step-by-step explanation:
The average speed of gas molecules is given by:
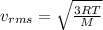
R is the gas constant, T is the temperature and M the molar mass of the gas.
We know that a water molecule has a mass that is 18 times that of a hydrogen atom:
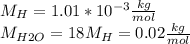
So, we have:
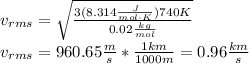
The water molecule cannot escape, since the average velocity of the water molecules is less than one sixth of the escape velocity of venus: