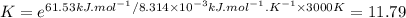Answer:
At 2000 K. K: 0.747
At 3000 K. K: 11.79
Step-by-step explanation:
Let's consider the decomposition of a generic diatomic element in its standard state.
1/2 X₂(g) ⟶ X(g)
The relation between the equilibrium constant (K) and the standard Gibbs energy (ΔG°) is:
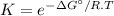
where,
R is the ideal gas constant (8.314 × 10⁻³ kJ/mol.K)
T is the absolute temperature
At 2000 K (ΔG° = 4.84 kJ·mol⁻¹)
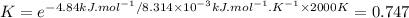
At 3000 K (ΔG° = −61.53 kJ·mol⁻¹)