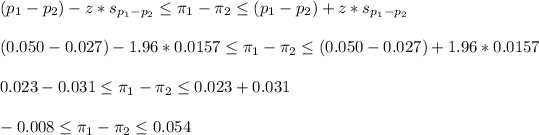Answer:
a) In hypothesis testing the null hypothesis is never accepted. It is rejected or not rejected. In this case, couldn't be rejected, so it is possible that both machines produce the same fraction of defective parts. It is reasonable to conclude that both machines produce the same fraction of defective parts, although this test doesn't conclude this.
b) P-value = 0.143
c)
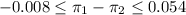
Explanation:
In this problem we have to do a Test of Differences between Proportions
The first step is to state the null and alternative hypothesis

The null hypothesis represents the case where both machines are expected to produce the same amount of defective parts.
The second step is determine the significance level. In this case is α=0.05.
The third step is to calculate the difference in the proportions
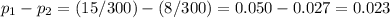
The fourth step is to estimate the standard deviation of the difference between proportions.
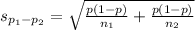
As
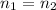 , we can calculate p as
, we can calculate p as
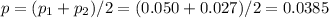 .
.
Then:

The fifth step is to compute p, the probability (or probability value).
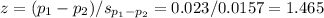
A z table can be used to find that the two-tailed probability value for a z=1.465 is P(x>|z|)=0.143.
The probability value (P-value) is 0.143. As it is bigger than the significance level (0.05), the effect is not significant. We can not reject the hypothesis.
To construct a 95% CI we can write:

For a 95% CI, z=1.96. The estimated standard deviation is the same calcaulated before. Now we can calculate: