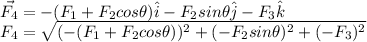Step-by-step explanation:
Assuming that all forces extend from the origin point, with
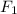 and
and
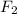 lying in the xy plane, so
lying in the xy plane, so
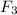 is along the z axis. So, we have:
is along the z axis. So, we have:
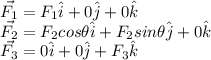
The net force is:
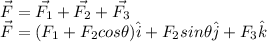
The force (
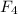 ) that would exactly counterbalance these three forces will be opposite in direction and equal in magnitude to the net force:
) that would exactly counterbalance these three forces will be opposite in direction and equal in magnitude to the net force: