Answer:
31.8 Joules is the the energy of the photon of light that was absorbed.
Step-by-step explanation:
Initially the electron is present at energy level equal to -50.3 Joules and on absorbing an energy it jumps to energy level which has energy of -18.5 Joules.
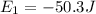 (Initial)
(Initial)
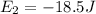 (Final)
(Final)
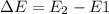
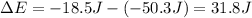
ΔE , here is also the energy of the photon absorbed by an electron before transition.
31.8 Joules is the the energy of the photon of light that was absorbed.