Answer:
(i) +3.
(ii) Mn.
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
(i)
Based on the diatomic ion, we solve for the unknown oxidation state of carbon, assuming that the oxygen works with -2, by a change balance:
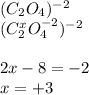
(ii)
We first must each ion's oxidation states as follows:
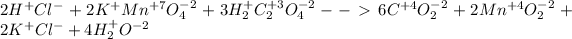
Then, for the reduction half reaction we identify the manganese as the element decreasing its oxidation state based on:
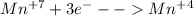
In addition, the carbon is oxidized from +3 to +4 (increase the oxidation state).
Kind regards.