Answer:
K = 36 J
Step-by-step explanation:
In this exercise we must use the conservation of mechanical energy at two points at initial x = 0 and the end point of maximum compression of the spring
Initial x = 0
Em₀ = K = ½ m v²
Final point of maximum compression
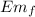 = Ke = ½ k x²
= Ke = ½ k x²
Em₀ =
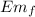
K = ½ k x²
We put the kinetic energy because it is a data, let's look for the spring constant
k = 2 K / x²
k = 2 9 / d²
k = 18 / d²
Let's calculate the kinetic energy, so that the compression is x = 2d
K = ½ k x²
K = ½ (18 / d²) (2d)²
K = ½ 18/d² 4d²
K = 36 J