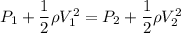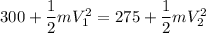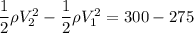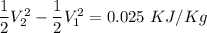Answer:
Change in kinetic energy=0.025\ KJ/Kg[/tex]
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that
P₁=300 KPa
P₂=275 KPa
Density of water
ρ = 1000 kg/m³
Change in kinetic energy of per unit mass mass given as
Lets take initial velocity V₁ and final velocity V₂
From energy conservation