Answer : The percentage error will be, 4.74%
Explanation :
Boyle's Law : It is defined as the pressure of the gas is inversely proportional to the volume of the gas at constant temperature and number of moles.
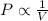
or,
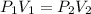
where,
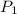 = first pressure = 660 mmHg
= first pressure = 660 mmHg
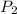 = second pressure = 780 mmHg
= second pressure = 780 mmHg
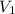 = first volume = 47.4 mL
= first volume = 47.4 mL
Note : (The value of first volume might be 47.4 mL because the difference between the value of first and second volume can not be more.)
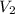 = second volume = ?
= second volume = ?
Now put all the given values in the above equation, we get:
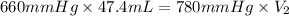
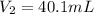
Thus, the value of second volume is, 40.1 mL
Now we have to calculate the percent error.
To calculate the percentage error, we use the equation:
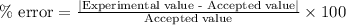
We are given:
Experimental value of volume = 38.2 mL
Accepted value of volume = 40.1 mL
Putting values in above equation, we get:
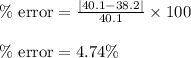
Hence, the percentage error will be, 4.74%