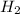Answer:
A.
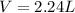 of
of
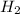
Step-by-step explanation:
1. First take the balanced chemical equation to obtain hydrogen gas:
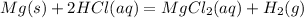
2. Find the limiting reagent to how much hydrogen is formed:
Take the number of moles of each compound and divide it between the stoichiometric coefficient in the balanced chemical equation.
- For the Mg:
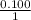
- For the HCl:
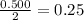
The magnesium is the limiting reagent.
3. Find the number of moles of hydrogen produced:
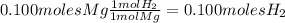
4. Find the volume of hydrogen using the ideal gas equation at STP:
The ideal gas equation is expressed as
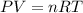 , where P is the pressure, at STP P=1 atm, V is the volume, n is the number of moles, R is a constante whose value is R=0.08206
, where P is the pressure, at STP P=1 atm, V is the volume, n is the number of moles, R is a constante whose value is R=0.08206
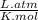 , and T is the temperature, at STP T=273K
, and T is the temperature, at STP T=273K
Solving for V:
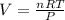
Replacing values:
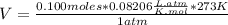
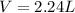 of
of