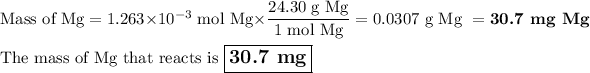Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
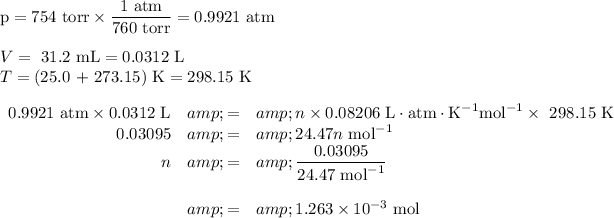
(a) Calculate the moles of H₂
We can use the ideal gas law:
pV = nRT
Data:
p = 754 torr
V = 31.2 mL
R = 0.082 06 L·atm·K⁻¹mol⁻¹
T = 25.0 °C K
Calculation:
(b) Calculate the moles of Mg
MM: 24.30
Mg + 2HCl ⟶ MgCl₂ + H₂
n/mol: 1.263 × 10⁻³

(c) Calculate the mass of Mg