Answer:
Volume of hydrogen gas formed under given condition is 135.94 L.
Volume of hydrogen gas formed at STP will be 14.03 liters.
Step-by-step explanation:
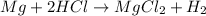
Moles of magnesium =
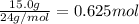
According to reaction, 1 mole of magnesium solid gives 1 mol of hydrogen gas.
Then 0.625 mol of magnesium solid will give =:
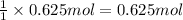 of hydrogen gas.
of hydrogen gas.
Moles of hydrogen gas formed = n = 0.625 moles
Temperature of the gas = T = 22.3 °C =295.45 K
Pressure of the gas = P = 11.3 kPa = 0.11152 atm
(1 atm = 101.325 kPa )
Volume of the gas
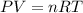 (ideal gas equation)
(ideal gas equation)
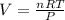
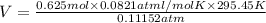
V = 135.94 L
Volume of hydrogen gas formed under given condition is 135.94 L.
Volume of hydrogen gas that would have formed in this reaction had it been conducted under standard temperature and pressure conditions.
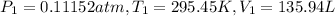
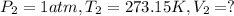
Using the combined gas equation :
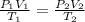
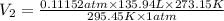
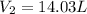
Volume of hydrogen gas formed at STP will be 14.03 liters.