Answer:
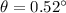
Step-by-step explanation:
It is given that,
Wavelength in vacuum,
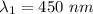
Wavelength in vacuum,
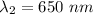
Refractive index for air,
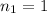
First refractive index,
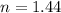
Second refractive index,
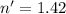
A ray is incident at an angle of incidence of 50 degrees. Let r is the angle of refraction. Firstly calculating the angle of refraction for two values of wavelength from Snell's law as :
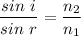
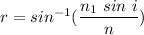
For 450 nm,
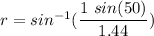
r = 32.13 degrees
For 650 nm,
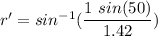
r' = 32.65 degrees
Let
 is the angle of dispersion between the two refracted rays in the oil such that,
is the angle of dispersion between the two refracted rays in the oil such that,
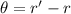
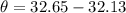
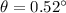
So, the angle of dispersion between the two refracted rays in the oil is closest to 0.52 degrees.