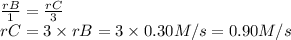Answer:
rA = 0.60 M/s
rC = 0.90 M/s
Step-by-step explanation:
Let's consider the following reaction:
2 A+B ⇒ 3 C
The rate of each substance can be calculated like the change in its concentration divided by the change in time. Given the rate must always be positive, we add a minus sign before the reactants change in concentration.
![rA=-(\Delta[A] )/(\Delta t)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/850ex66aew3ccojse2qtt0x9qdre9r5w3j.png)
![rB=-(\Delta[B] )/(\Delta t)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/18pgp4rn4yg67fe7w1ojruje68hwxscr90.png)
![rC=(\Delta[C] )/(\Delta t)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/u36pexqhqqmtmyfp738bzszkgo5sp5y5fr.png)
The rate of the reaction is equal to the rate of each substance divided by its stoichiometric coefficient.

The rate of disappearance of B is 0.30 M/s.
The rate of disappearance of A is:
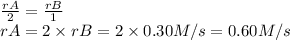
The rate of appearance of C is: