Answer
given,
mass of the shuffleboard disk = 0.42 kg
speed of the cue is increased to = 4.2 m/s
acceleration takes over 2 m then acceleration is zero.
the disk additionally slide to 12 m
final speed of disk = 0 m/s
a) increase in thermal energy
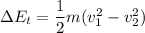
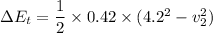
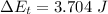
b)
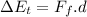
F_f is the frictional force
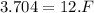
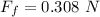
increase in thermal energy for entire movement of 14 m
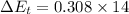
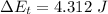
c) Work done on the disk by the cue
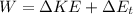
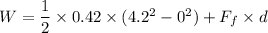
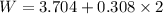
W = 3.704 + 0.616
W = 4.32 J