Answer : The initial concentration of HI and concentration of
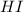 at equilibrium is, 0.27 M and 0.386 M respectively.
at equilibrium is, 0.27 M and 0.386 M respectively.
Solution : Given,
Initial concentration of
 and
and
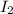 = 0.11 M
= 0.11 M
Concentration of
 and
and
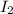 at equilibrium = 0.052 M
at equilibrium = 0.052 M
Let the initial concentration of HI be, C
The given equilibrium reaction is,
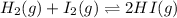
Initially 0.11 0.11 C
At equilibrium (0.11-x) (0.11-x) (C+2x)
As we are given that:
Concentration of
 and
and
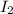 at equilibrium = 0.052 M = (0.11-x)
at equilibrium = 0.052 M = (0.11-x)
0.11 - x = 0.052
x = 0.11 - 0.052
x = 0.058 M
The expression of
 will be,
will be,
![K_c=([HI]^2)/([H_2][I_2])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/wc73goz3xvwpin96d8csmq8762t2meimob.png)
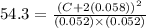
By solving the terms, we get:
C = 0.27 M
Thus, initial concentration of HI = C = 0.27 M
Thus, the concentration of
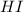 at equilibrium = (C+2x) = 0.27 + 2(0.058) = 0.386 M
at equilibrium = (C+2x) = 0.27 + 2(0.058) = 0.386 M