Answer:
We reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternate hypothesis. Thus, it be concluded that the population mean is less than 20.
Explanation:
We are given the following in the question:
Population mean, μ = 60
Sample mean,
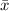 = 19.5
= 19.5
Sample size, n = 60
Alpha, α = 0.05
Population standard deviation, σ = 1.8
First, we design the null and the alternate hypothesis
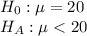
We use One-tailed z test to perform this hypothesis.
Formula:
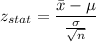
Putting all the values, we have
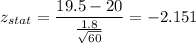
Now,
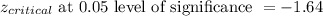
Since,
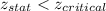
We reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternate hypothesis. Thus, it be concluded that the population mean is less than 20.