Answer:
The drift velocity of the electrons in this case is c) 5.52 x 10-4 m/s
Step-by-step explanation:
Hi
First of all, we need to find the volume occupied by 63.3g of copper, so
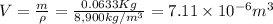 , then if we assume each atom of copper contributes with one free electron to the material body
, then if we assume each atom of copper contributes with one free electron to the material body
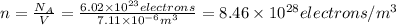 .
.
Finally, we apply
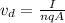 , where A is area so,
, where A is area so,
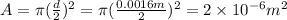 , thus
, thus
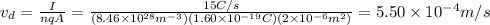 .
.
As we can see c. 5.52 x 10-4 m/s is the nearest one.