Answer:
(a) 14 hours is the half life.
(b) The rate constant, k = 0.0495 hour⁻¹
(c) The rate constant, k = 5.36 mg/L.hour⁻¹
(d) The kinetics of a reaction can be known graphically by plotting the concentration vs time experimental data on a sheet of graph.
Step-by-step explanation:
(a) Given that:-
Initial concentration = 150 mg/L
Final concentration = 75 mg/L (Half)
Time taken = 14 hours
Half life is the time at which the concentration of the reactant reduced to half. So, 14 hours is the half life.
(b) Half life expression for first order kinetic is:
Half life = 14.0 hours
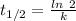
Where, k is rate constant
So,
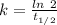

The rate constant, k = 0.0495 hour⁻¹
(c) Half life expression for zero order kinetic is:
Half life = 14.0 hours
![t_(1/2)=([A]_0)/(2k)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/8xrm9cgbcwaoi76xiinui2x60hsetmhjel.png)
Where, k is rate constant
![[A]_0](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/1z3zdal3zhydky3w24hmgrwjngt8hmnwl0.png) is the initial concentration = 150 mg/L
is the initial concentration = 150 mg/L
So,

The rate constant, k = 5.36 mg/L.hour⁻¹
(d) The kinetics of a reaction can be known graphically by plotting the concentration vs time experimental data on a sheet of graph.
The concentration vs time graph of zero order reactions is linear with negative slope.
The concentration vs time graph for a first order reactions is a exponential curve.
The concentration vs time graph for a second order reaction is a hyberbolic curve.