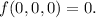Answer:
Maximum attained at point
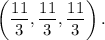
Minimum attained at point
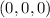
Explanation:
Write f(x,y,z) as
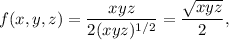
and let
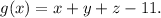
We have to optimize the function f(x,y,z) subject to g(x,y,z)=0. Using Lagrange multipliers, we have to solve the system of equations below:
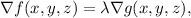
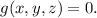
Or equivalently:
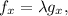
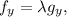
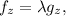
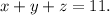
Now we calculate the partial derivatives of f and g:
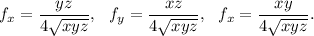
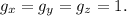
Then we have to solve the system of equations
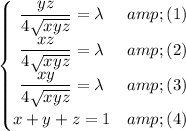
From equation (1) and (2) we get by cancelling the common factor
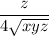 that x = y.
that x = y.
Similarly, using (2) and (3) we get that y = z. Therefore, we have that x = y = z, and by equation (4), we obtain that
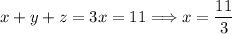
Since the function f(x,y,z) is non-negative, then
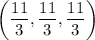 is a point where f attains an absolute maximum, and
is a point where f attains an absolute maximum, and
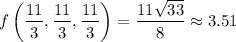
Because of the non-negativity of the function, we see that at
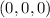 f attains an absolute minimum, and its value is
f attains an absolute minimum, and its value is