Answer:
1,57 x 10-3 mol de CO2
Step-by-step explanation:
The general equation of ideal gases can be used to solve the problem. Previously, the units of the supplied data must be converted in order to use this equation.
1- Use conversion factor to keep all data in the same units:
Atmospheric pressure:
760.0 torr _____ 1 atm
728.0 torr _____ X = 0.9579 atm
Calculation:
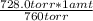
Temperature:
T (K) = t (° C) + 273.15 = 25.8 ° C + 273.15 = 298, 95 K
Volume of gas obtained:
1000 mL CO2 _____ 1 L
40.16 mL CO2 _____ X = 0.04016 L
Calculation:
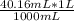
2- Now, using the general equation of ideal gases, you can clear and calculate the number of moles obtained from CO2 gas:
If: PxV = n x R x T
So:
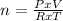
Where:
• P: Gas pressure in atm
• V: Volume of gas in L
• N: Number of moles of gas
• R: Gas constant (L.atm / mol.K)
• T: Temperature in K
3- Placing the values and solving the equation, the result is obtained:
n = (0.9579 atm x 0.04016 L) / (0.08206 L.atm / mol.K x 298.95 K) = 0.0015681 mol of CO2
If the result becomes scientific notation, it is equal to 1, 57 x 10-3 mol
Therefore, 1.57 x 10-3 moles of CO2 were produced