Answer:
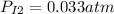
Step-by-step explanation:
Hi, the first step is to calculate how much F2 there is in the container:
Fluorine can be considered as an ideal gas (given that is non-polar and has a small molecule). Using the ideal gas formula:
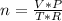
Where:
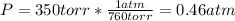
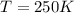
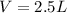
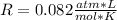
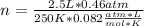
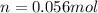
Now, the mols of iodine:
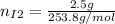
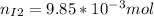
The chemical reaction described is the following:
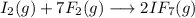
In this case, the limitant reactant is the fluorine:
1) The 0.056 mol of F2 gives
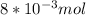 of
of
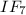 and consumes
and consumes
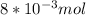 of I2.
of I2.
2) At the end, in the conteiner we have:
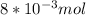 of
of
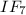
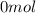 of
of
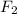
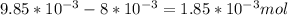 of
of
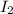
In total:
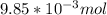 .All in 2.5 L at 550 K
.All in 2.5 L at 550 K
The final pressure:
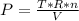
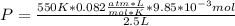
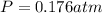
The partial pressure:
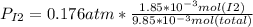
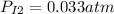
Note: this partial pressure is calculated by the Dlaton's principle