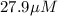Answer : The value of
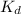 for the receptor-ligand interaction is
for the receptor-ligand interaction is
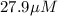
Explanation :
The equilibrium reaction between receptor and ligand will be:
![R+L\overset{K_f}\rightarrow [RL]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/biology/college/tywwfyugz7r6vq3wz96d0ghh29xlldpesk.png) (forward reaction)
(forward reaction)
![[RL]\overset{K_d}\rightarrow R+L](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/biology/college/nthztxknd3qkwqjn0frv335xelfcvhe7sl.png) (backward reaction)
(backward reaction)
where,
R = receptor
L = ligand
[RL] = receptor-ligand complex
As we know that,
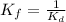
The expression of
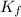 is:
is:
![K_f=([RL])/([R][L])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/biology/college/n6hfrnknnew4zk89lz4x5yb3nvcf6d6en8.png)
As we are given that:
Total [R] =
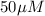
Total [L] =
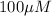
Free [R] =
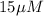
Bound [R] =
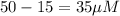
Bound [L] = Bound [R] =
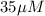
Free [L] =
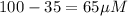
Now put all the given values in above expression, we get:
![K_f=([RL])/([R][L])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/biology/college/n6hfrnknnew4zk89lz4x5yb3nvcf6d6en8.png)
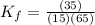
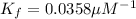
Now we have to calculate the value of
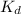 for the receptor-ligand interaction.
for the receptor-ligand interaction.
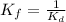
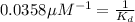
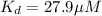
Therefore, the value of
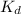 for the receptor-ligand interaction is
for the receptor-ligand interaction is