Answer:
We accept the alternate hypothesis and conclude that mean SAT score for Stevens High graduates is not the same as the national average.
Explanation:
We are given the following in the question:
Population mean, μ = 510
Sample mean,
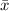 = 502
= 502
Sample size, n = 60
Sample standard deviation, s = 30
Alpha, α = 0.05
First, we design the null and the alternate hypothesis
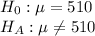
We use Two-tailed t test to perform this hypothesis.
Formula:
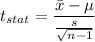 Putting all the values, we have
Putting all the values, we have
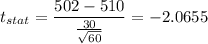
Now,
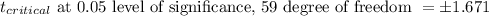
Since,
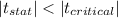
We reject the null hypothesis and fail to accept it.
We accept the alternate hypothesis and conclude that mean SAT score for Stevens High graduates is not the same as the national average.