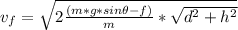Answer:
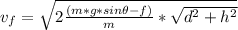
Step-by-step explanation:
Known data
m= mass of the block
h= high of the wedge
d= length of the wedge
θ = angle θ of the wedge with respect to the horizontal direction
f = force of kinetic friction between the block and the wedge
g = 9.81 m/s² : acceleration due to gravity
Newton's second law:
∑F = m*a Formula (1)
∑F : algebraic sum of the forces in Newton (N)
m : mass in kilograms (kg)
a : acceleration in meters over second square (m/s²)
We define the x-axis in the direction parallel to the movement of the block on the wedge and the y-axis in the direction perpendicular to it.
Calculated of the weight
W= m*g
x-y weight components
Wx= Wsin θ= m*g*sin θ
Wy= Wcos θ =m*g*cos θ
We apply the formula (1) to calculated acceleration of the block:
∑Fx = m*ax , ax= a : acceleration of the block
Wx-f = m*a
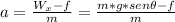
Kinematics of the block
Because the block moves with uniformly accelerated movement we apply the following formula to calculate the final speed of the block :
vf²=v₀²+2*a*X Formula (2)
Where:
X:displacement
v₀: initial speed
vf: final speed
a: acceleration
Data
v₀=0
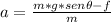
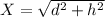
We replace data in the formula (2)
vf²=v₀²+2*a*X
vf²=0+2*a*X