Step-by-step explanation:
As the given reaction is as follows.
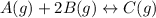
The given data is as follows.
Initially,
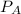 = 0.109 atm,
= 0.109 atm,
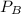 = 0.109 atm,
= 0.109 atm,
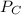 = 0.109 atm
= 0.109 atm
And, at equilibrium
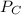 = 0.047 atm
= 0.047 atm
Therefore, change in
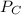 will be calculated as follows.
will be calculated as follows.
0.109 - 0.047
= 0.062 atm
Hence,
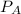 = (0.109 + 0.062) atm = 0.171 atm
= (0.109 + 0.062) atm = 0.171 atm
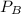 =
=
![[0.109 + (2 * 0.062)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/gh2o5u6rn02oggwlv7abm4wt4gnhapmi0w.png) atm
atm
= 0.233 atm
Now, calculate the value of
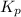 as follows.
as follows.
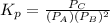
=
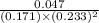
= 5.06
Also, we known that
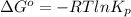
Hence, calculate the value of
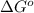 as follows.
as follows.
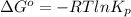
=
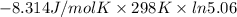
=
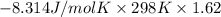
= -4017.05 J/mol
or, = -4.017 kJ/mol (as 1 kJ = 1000 J)
Thus, we can conclude that the value of
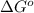 for the given reaction is -4.017 kJ/mol.
for the given reaction is -4.017 kJ/mol.