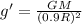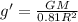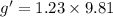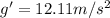Answer:
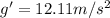
Step-by-step explanation:
As we know that the acceleration due to gravity is given as
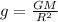
now for earth we know that
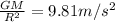
now if on the surface of another planet we know that the mass is same as that the mass of Earth but radius is 10% less than the radius of Earth
so we have
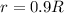
so we will have