Answer:
Cu is oxidized and H₂ is reduced.
Step-by-step explanation:
Given chemical equation,
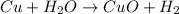
On observing the equation, if we write the oxidation states of all elements in the compounds, we will get
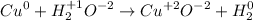
In this equation,
Oxidation number of 'Cu' is increased from 0 to 2. Hence it is oxidized. While the oxidation number of 'H₂' is decreased from +1 to 0. Hence it is reduced.