Answer:
a)
[0.5235, 0.5765]
To interpret this result, we could say there is a 99% of probability that the proportion of American adults who have watched digitally streamed TV programming on some type of device is between 52.35% and 57.65%
b) 1,843 American adults
Explanation:
The 99% confidence interval is given by
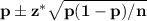
where
p = the proportion of American adults surveyed who said they have watched digitally streamed TV programming on some type of device = 55% = 0.55
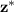 the z-score for a 99% confidence level associated with the Normal distribution N(0,1). We can do this given that the sample size (2,341) is big enough
the z-score for a 99% confidence level associated with the Normal distribution N(0,1). We can do this given that the sample size (2,341) is big enough
n = sample size = 2,341
We can find the
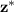 value either with a table or with a spreadsheet.
value either with a table or with a spreadsheet.
In Excel use NORM.INV(0.995,0,1)
In OpenOffice Calc use NORMINV(0.995;0;1)
We get a value of
 = 2.576
= 2.576
and our 99% confidence interval is
![\bf 0.55\pm 2.576√(0.55*0.45/2341)=0.55\pm 2.576*0.0103=0.55\pm 0.265 = [0.5235, 0.5765]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/rsdxrrh957cy8zghrev6jtk8box1mmesci.png)
To interpret this result, we could say there is a 99% of probability that the proportion of American adults who have watched digitally streamed TV programming on some type of device is between 52.35% and 57.65%
We are 99% confident that this interval contains the true population proportion.
(b) What sample size would be required for the width of a 99% CI to be at most 0.03 irrespective of the value of p?? (Round your answer up to the nearest integer.)
The sample size n in a simple random sampling is given by
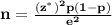
where
e is the error proportion = 0.03
hence
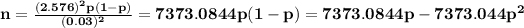
taking the derivative with respect to p, we get
n'(p)=7373.0844-2*7373.0844p
and
n'(p) = 0 when p=0.5
By taking the second derivative we see n''(p)<0, so p=0.5 is a maximum of n
This means that if we set p=0.5, we get the maximum sample size for the confidence level required for the proportion error 0.03
Replacing p with 0.5 in the formula for the sample size we get
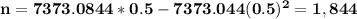
rounded up to the nearest integer.