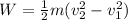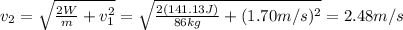Answer:
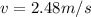
Step-by-step explanation:
From work-energy theorem we got that:
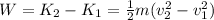 (1)
(1)
If we see the free body diagram attached we can calculate the work done by the group of students by knowing its definition given by:

Where F is Force and s is distance
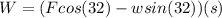
These are the forces at the x-axis that are causing the work done by the students
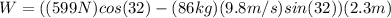
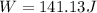
Now, we can calculate the velocity at the top of the ramp using (1)