Answer:
-0.1 Joules
Step-by-step explanation:
Here, the kinetic energy of the spring and glider is conserved.
So, we get
KE of spring + Work done by friction = Change in momentum of glider
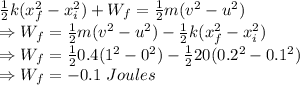
The work done by friction during that segment of motion is -0.1 Joules