Answer:
53.7 %
Explanation:
Given:
Number of trials,
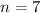
Number of successes,
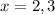
Probability of success,
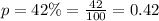
Therefore, probability of failure,
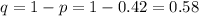
The Bernoulli's distribution for
 successes out of
successes out of
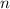 trials is given as:
trials is given as:
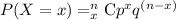
So, probability of 2 or 3 successes is given as:
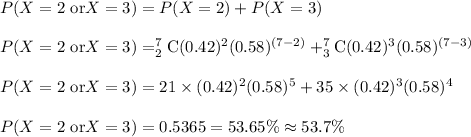
Therefore, the probability of 2 or 3 successes in 7 trials of a binomial experiment is 53.7 %.