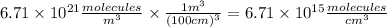Answer:
a)
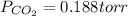
b)
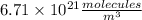
c)
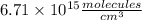
Step-by-step explanation:
a) The partial pressure of CO₂ is given by:
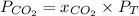
Since the molar fraction of the gas is directly proportional to the volume of the gas, the molar fraction is given by:
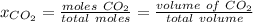
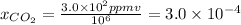
Hence,
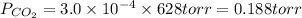
b) Using the Ideal Gas Law, we can find the number of moles of CO₂:
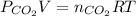
where:
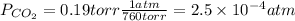
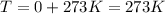
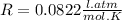
The concentration of CO in molecules per cubic meter is:
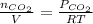
c) The concentration of CO in molecules per cubic centimeter is: