Answer:
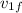 = -0.460 m/s
= -0.460 m/s
Step-by-step explanation:
To solve this problem we will use the concept of moment, write the initial amount when they are united and the end
Initial. Before break away
p₀ = (m + m) v₀
Final. After separating
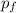 = m
= m
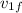 + m
+ m
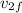
p₀ =
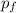
(m + m) v₀ = m
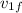 + m
+ m
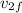
They tell us that when they go together the speed vo = 0.420 m / s and after separating one we will call 2 has a speed of v2f = 1,300 m / s. let's look for each other's speed
m
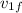 = (2m) vo - m
= (2m) vo - m
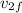
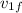 = 2 v₀ -
= 2 v₀ -
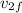
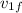 = 2 0.420 - 1.300
= 2 0.420 - 1.300
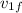 = -0.460 m/s
= -0.460 m/s
The negative sign indicates that it moves to the left