Answer: 9.9 grams
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the moles, we use the equation:
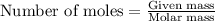
a) moles of

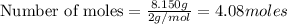
b) moles of
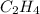
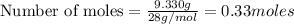
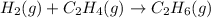
According to stoichiometry :
1 mole of
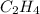 combine with 1 mole of
combine with 1 mole of

Thus 0.33 mole of
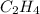 will combine with =
will combine with =
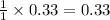 mole of
mole of

Thus
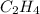 is the limiting reagent as it limits the formation of product.
is the limiting reagent as it limits the formation of product.
As 1 mole of
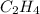 give = 1 mole of
give = 1 mole of
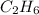
Thus 0.33 moles of
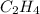 give =
give =
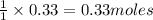 of
of
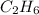
Mass of
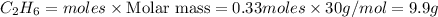
Thus theoretical yield (g) of
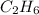 produced by the reaction is 9.9 grams
produced by the reaction is 9.9 grams