Answer:
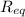 = 19 Ω, I = 0.105 A, V1 = 1.05 V and V2 = 0.95 V
= 19 Ω, I = 0.105 A, V1 = 1.05 V and V2 = 0.95 V
Step-by-step explanation:
The correct way to solve this type of problem is to find the current or voltage values for the equivalent resistance and from here find the other values.
For a series circuit the equivalent resistance is the sum of the resistance
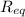 = R1 + R2
= R1 + R2
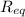 = 10 +9
= 10 +9
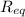 = 19 Ω
= 19 Ω
Let's use the equation for the voltage
V = I
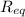
I = V /
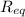
I = 2/19
I = 0.105 A
In a series circuit the current is constant, so let's use the voltage equation for each resistor
V1 = I R1
V1 = 0.105 10
V1 = 1.05 V
V2 = 0.105 9
V2 = 0.95 V
Note that the sum of this voltage is the total voltage applied.