Answer:
From Second law of Newtons:
It states that rate of change of linear momentum is equal to the total external force.
We can say that
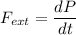
Linear momentum P
P = m v
m=Mass ,v =velocity
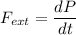
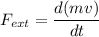
If mass is not varying with time
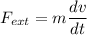
We know that acceleration a
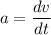
So
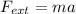
Again
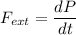
If External force is zero then
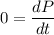
It means that P is not varying with time and it is constant.
So
Pi = Pf ( Initial linear momentum = Final linear momentum)
Linear momentum is conserve.