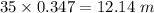Answer:
The horizontal distance covered is 12.14 m
Solution:
As per the question:
Charge on the particle, q = 1.7 C
Mass of the particle, m = 1.6 kg
Separation distance between the plates, d = 4.5 m
Electric field strength, E = 26 N/C (towards negative Y-axis)
Initial velocity of the particle, v = 35 m/s
Now,
To calculate the horizontal distance of the particle before striking:
Since, the electrostaic force and the force due to gravity both acts on the particle in the vertically downward direction and is given by:
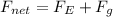 (1)
(1)
where
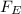 = qE = Force due to electric field or electrostatic force on the particle
= qE = Force due to electric field or electrostatic force on the particle
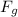 = mg = Force due to gravity on the particle
= mg = Force due to gravity on the particle
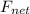 = ma
= ma
where
a = acceleration of the particle
Now, from eqn (1)
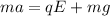
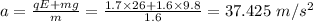
Now, since the particle starts halfway vertically:
y =
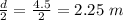
Now,
The time taken by the particle to cover the distance 'y' with constant acceleration is given by kinematic eqn:
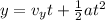
Since, the particle starts from rest
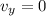
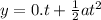
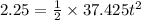
t = 0.347 s
The distance covered by the particle in the horizontal direction is given by:
x = vt =