Answer:
a)Both X and Y can be well approximated by normal random variables.
Explanation:
For each individual, there are only two possible outcomes. Either they are right-handed, or they are left-handed. This means that we can solve this problem using concepts of the binomial probability distribution.
Binomial probability:
Probability of exactly x sucesses on n repeated trials, with probability p.
The binomial probability can be well approximated by normal random variables, using the expected value
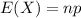 and the standard deviation
and the standard deviation
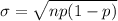
Let X be the number of males (out of the 100) who are left-handed.
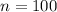 and
and
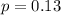 . Can be well approximated.
. Can be well approximated.
Let Y be the number of females (out of the 80) who are left-handed.
 and
and
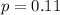 . Can be well approximated.
. Can be well approximated.
The correct answer is
a)Both X and Y can be well approximated by normal random variables.