Answer:
The probability that a stock will show an increase in its closing price on seven consecutive days is 0.78%.
Explanation:
In each day, there are only two possible outcomes for the stock. Either it increases, or it decreases. This means that we can solve this problem using concepts of the binomial probability distribution.
Binomial probability distribution
The binomial probability is the probability of exactly x successes on n repeated trials, and X can only have two outcomes.
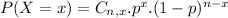
In which
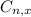 is the number of different combinatios of x objects from a set of n elements, given by the following formula.
is the number of different combinatios of x objects from a set of n elements, given by the following formula.
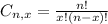
And p is the probability of X happening.
In this problem, we have that
There are 7 days, so
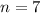 .
.
The increase or decrease in the price of a stock between the beginning and the end of a trading day is assumed to be an equally likely random event. This means that
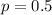 .
.
What is the probability that a stock will show an increase in its closing price on seven consecutive days?
This is
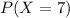
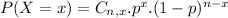
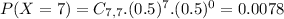
The probability that a stock will show an increase in its closing price on seven consecutive days is 0.78%.