Answer:
Yes, double cosets partition G.
Explanation:
We are going to define a relation over the elements of G.
Let
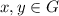 . We say that
. We say that
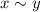 if, and only if,
if, and only if,
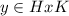 , or, equivalently, if
, or, equivalently, if
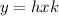 , for some
, for some
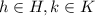 .
.
This defines an equivalence relation over G, that is, this relation is reflexive, symmetric and transitive:
- Reflexivity: (
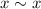 for all
for all
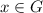 .) Note that we can write
.) Note that we can write
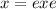 , where
, where
 is the identity element, so
is the identity element, so
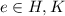 and then
and then
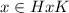 . Therefore,
. Therefore,
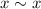 .
. - Symmetry: (If
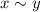 then
then
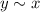 .) If
.) If
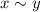 then
then
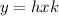 for some
for some
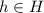 and
and
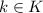 . Multiplying by the inverses of h and k we get that
. Multiplying by the inverses of h and k we get that
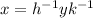 and is known that
and is known that
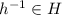 and
and
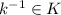 . This means that
. This means that
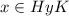 or, equivalently,
or, equivalently,
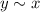 .
.
- Transitivity: (If
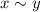 and
and
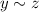 , then
, then
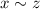 .) If
.) If
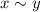 and
and
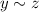 , then there exists
, then there exists
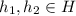 and
and
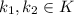 such that
such that
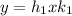 and
and
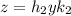 . Then,
. Then,
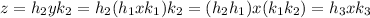 where
where
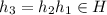 and
and
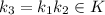 . Consequently,
. Consequently,
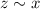 .
.
Now that we prove that the relation "
 " is an equivalence over G, we use the fact that the different equivalence classes partition G. Since the equivalence classes are defined by
" is an equivalence over G, we use the fact that the different equivalence classes partition G. Since the equivalence classes are defined by
![[x]=\{y\in G\colon x\sim y\} =\{y\in G \colon y=hgk\ \text{for some } h\in H, k\in K \}=HxK](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/high-school/ikmvh0cgicxsed0oem5au5q1syct2hu5vs.png) , then we're done.
, then we're done.