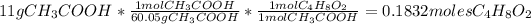Answer:
0.1832 moles of ethyl acetate (
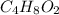 )
)
Step-by-step explanation:
1. Find the balanced chemical equation:
In the production of ethyl acetate, the acetic acid
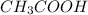 reacts with ethanol to produce ethyl acetate
reacts with ethanol to produce ethyl acetate
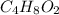 and water, that is:
and water, that is:
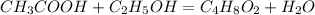
2. Find the theoretical maximum moles of ethyl acetate
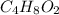 :
:
As the problem says that the acetic acid
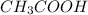 is the limiting reagent, use stoichiometry to find the moles of ethyl acetate produced:
is the limiting reagent, use stoichiometry to find the moles of ethyl acetate produced: