Answer:
12.6 g
Step-by-step explanation:
The formula for the calculation of moles is shown below:
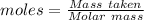
For butane:-
Mass of butane = 8.14 g
Molar mass of butane = 58.12 g/mol
The formula for the calculation of moles is shown below:
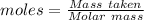
Thus,
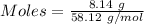
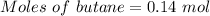
Given: For

Given mass = 41 g
Molar mass of
 = 31.9988 g/mol
= 31.9988 g/mol
The formula for the calculation of moles is shown below:
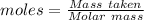
Thus,
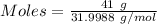
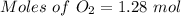
According to the given reaction:
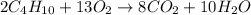
2 moles of butane react with 13 moles of oxygen
Also,
1 mole of butane react with 6.5 moles of oxygen
So,
0.14 mole of butane react with 6.5*0.14 moles of oxygen
Moles of oxygen = 0.91 moles
Available moles of
 = 1.28 moles (Extra)
= 1.28 moles (Extra)
Limiting reagent is the one which is present in small amount. Thus, butane is limiting reagent.
The formation of the product is governed by the limiting reagent. So,
2 moles of butane forms 10 moles of water
Also,
1 mole of butane forms 10 moles of water
So,
0.14 mole of butane forms 5*0.14 mole of water
Moles of water = 0.7 moles
Molar mass of water = 18 g/mol
So,
Mass of water= Moles × Molar mass = 0.7 × 18 g = 12.6 g