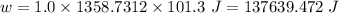Answer:
137639.472 J
Step-by-step explanation:
Given, Mass of water = 1 kg = 1000 g
Molar mass of water = 18.0153 g/mol
The formula for the calculation of moles is shown below:
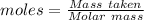
Thus,
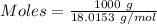
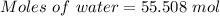
Pressure = 1.0 atm
Temperature = 25 °C
The conversion of T( °C) to T(K) is shown below:
T(K) = T( °C) + 273.15
So,
T₁ = (25 + 273.15) K = 298.15 K
Using ideal gas equation as:
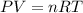
where,
P is the pressure
V is the volume
n is the number of moles
T is the temperature
R is Gas constant having value = 0.0821 L.atm/K.mol
Applying the equation as:
1.0 atm × V = 55.508 mol × 0.0821 L.atm/K.mol × 298.15 K
⇒V = 1358.7312 L
The expression for the calculation of work done by the surroundings is shown below as:
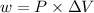
Where, P is the pressure
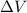 is the change in volume
is the change in volume
From the question,
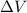 = 1358.7312 - 0 L = 1358.7312 L
= 1358.7312 - 0 L = 1358.7312 L
P = 1.0 atm
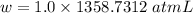
Also, 1 atmL = 101.3 J
So,