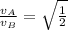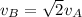Answer:
The velocity of cart B is
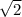 the velocity of cart A
the velocity of cart A
Solution:
As per the question:
Let the masses of both the carts A and B be 'm' kg
Distance traveled by both the carts be 'D' m
Force acting on A be 'F' N
Force acting on B be '2F' N
Now,
The relation between the velocities of A and B can be derived as :
Acceleration of cart A,
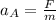
Acceleration of the cart B,
![a_(B) = (2F)/(m) = 2[tex][a_(A)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/physics/high-school/50akyxrb1dme82gdiy24rv6rgne287nx3c.png)
Now, using the third eqn of motion for both the carts A and B:
For cart A:
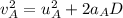
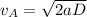
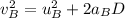
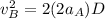
where
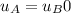 = initial velocity of cart A and cart B respectively
= initial velocity of cart A and cart B respectively
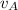 = final velocity of cart A
= final velocity of cart A
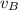 = final velocity of cart B
= final velocity of cart B
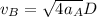
Now, dividing the velocities of the cart A and B: