Answer: Only 1 molecule of methane gas is required in the chemical equation.
Step-by-step explanation:
Law of conservation of mass states that mass can neither be created nor be destroyed but it can only be transformed from one form to another form. This also means that total number of individual atoms on reactant side must be equal to the total number of individual atoms on the product side.
Every balanced chemical equation follows law of conservation of mass.
The chemical equation for the reaction of methane and oxygen gas follows:
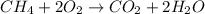
By Stoichiometry of the reaction:
1 molecule of methane gas reacts with 2 molecules of oxygen gas to produce 1 molecule of carbon dioxide gas and 2 molecules of water.
Hence, only 1 molecule of methane gas is required in the chemical equation.