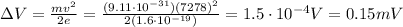Answer:
0.15 mV
Step-by-step explanation:
In order to exhibit wave nature, the de Broglie wavelength of the electron must be of the same size of the diameter of the pinhole, therefore:
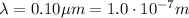
The de Broglie wavelength of an electron is
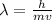
where
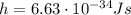 is the Planck constant
is the Planck constant
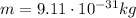 is the mass of the electron
is the mass of the electron
v is the electron's speed
Therefore, the electron's speed must be
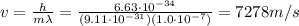
When accelerated through a potential difference
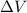 , the kinetic energy gained by the electron is equal to the change in electric potential energy, therefore
, the kinetic energy gained by the electron is equal to the change in electric potential energy, therefore
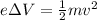
where
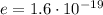 is the magnitude of the charge of the electron
is the magnitude of the charge of the electron
So, we can find the potential difference needed: