Answer:
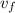 = √[2g (sin θ - μ cos θ) d ] and x = √ [2g d m/k (sin θ - μ cos θ)]
= √[2g (sin θ - μ cos θ) d ] and x = √ [2g d m/k (sin θ - μ cos θ)]
Step-by-step explanation:
We must solve this problem in parts, let's start by working with points A and B, we can use the principles of energy, in this case there is friction so let's use Newton's second law to find the acceleration of the body and with it the speed in the lowest point of the plane
The reference system has the x axis parallel to the plane and the axis and perpendicular, the weight is the only force that we must decompose
sin θ = Wₓ / W
cos θ =
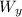 / W
/ W
Wₓ = W sin θ
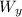 = W cos θ
= W cos θ
We write the equations on each axis
Y Axis
N-
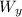 = 0
= 0
N =
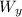
N = mg cos θ
X axis
Wₓ -fr = m a
Friction force is
fr = μ N
mg sin θ - μ mg cos θ = ma
a = g (sin θ - μ cos θ)
This is the acceleration along the plane. Let's use the kinematic equations to find the velocity in the lower part of the plane, as the body is initially at rest its zero velocity (vo = 0) and the distance traveled is the length of the plane (d)
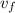 ² = v₀² + 2 a d
² = v₀² + 2 a d
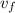 ² = 0 + 2 a d
² = 0 + 2 a d
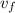 = √[2g (sin θ - μ cos θ) d ]
= √[2g (sin θ - μ cos θ) d ]
We already have the speed at point B
Now at point C it hits a spring and compresses it, we can use energy conservation to find the compression of the spring, let's write the mechanical energy at points C and D
Initial point C
Em₀ = K = ½ m v²
Final point D
Em₁ = Ke = ½ k x²
Em₀ = Em₁
½ m v² = ½ k x²
x² = m / k v²
x² = m / k 2 g (sin θ - μ cos θ) d
x = √ [2g d m/k (sin θ - μ cos θ)]