Step-by-step explanation:
Given that,
Mass of block = 50 kg
Friction less incline = 2.4 m
Diagonal height= 0.54 m
According to figure,
(a). We need to calculate the angle
Using formula of angle
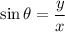
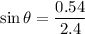
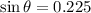
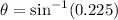
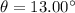
We need to calculate the force applied by the worker
Using formula of force
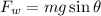
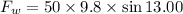
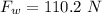
(b). We need to calculate the work done by the force applied by worker in opposite direction
Using formula of work done
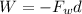
Put the value into the formula
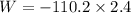
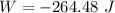
(c). We need to calculate the gravitational force
Using formula of gravitational force
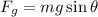
Put the value into the formula
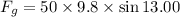
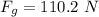
(d). We need to calculate the normal force on the block from the surface of the incline
The normal force acting on the block is perpendicular to distance traveled by the block.
So, the work done by the normal force is zero.
(e). We need to calculate the net force on the block
The block slides down with constant speed so the net force on the block is zero.
Hence, This is the required solution.